| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- LED
- LED 제어
- 스위치
- Generalized forward
- Interrupt
- Transport layer
- 펌웨어
- GPIO
- 신경망 첫걸음
- demultiplexing
- 인터럽트
- 디바이스 드라이버
- 모두를 위한 딥러닝]
- function call
- Network layer
- 밑바닥부터 시작하는 딥러닝
- 텐서플로우
- Switch
- Linux
- 딥러닝
- file descriptors
- Class Activation Map
- 신경망
- 운영체제
- RDT
- TensorFlow
- 모두를 위한 딥러닝
- Router
- 3분 딥러닝
- 리눅스
Archives
- Today
- Total
건조젤리의 저장소
6-2. Q-Network 구현 (Frozen Lake) 본문
김성훈 교수님의 강의내용을 정리한 내용입니다.
출처 : http://hunkim.github.io/ml/
모두를 위한 머신러닝/딥러닝 강의
hunkim.github.io

One-hot형식으로 상태값을 주게 되면 Action을 출력해주는 구조이다.

입력을 One-hot형식으로 바꿔주기 위해 identity함수를 이용해보자.

one_hot함수를 만들었다.

입력과 출력 크기를 설정하고, 이에 맞게 변수들을 설정해준다.
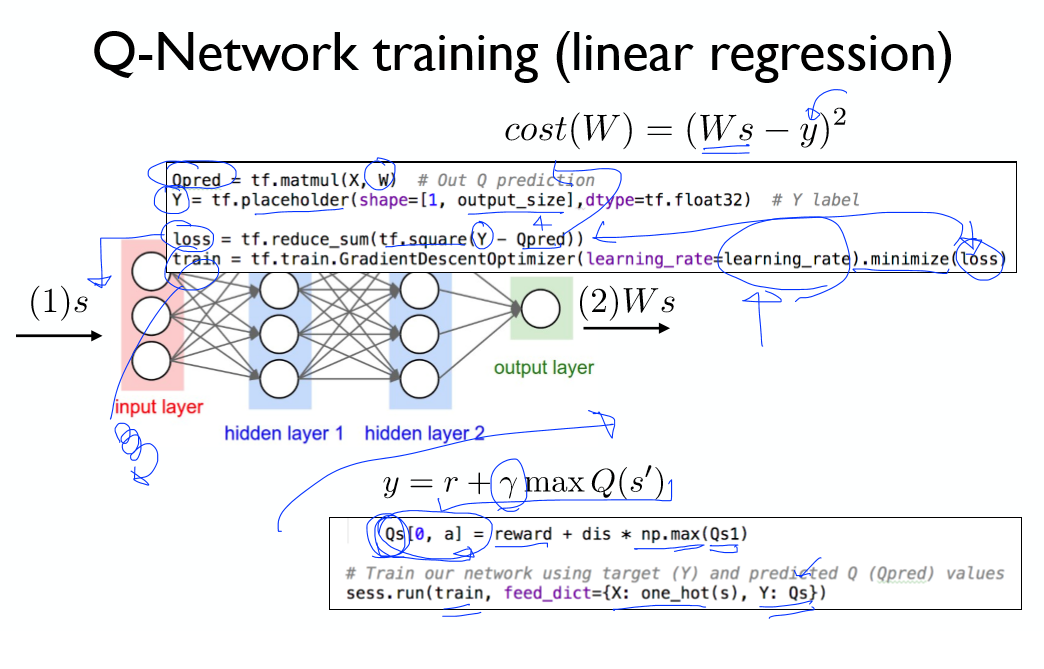
제곱오차를 사용하여 Cost함수를 만들고, 이를 경사하강법을 이용해 최소화 한다.
이때, 이용하는 y값은 위 그림을 참고하자.


e-greedy 방법을 사용하여 Actionn을 선택한다.
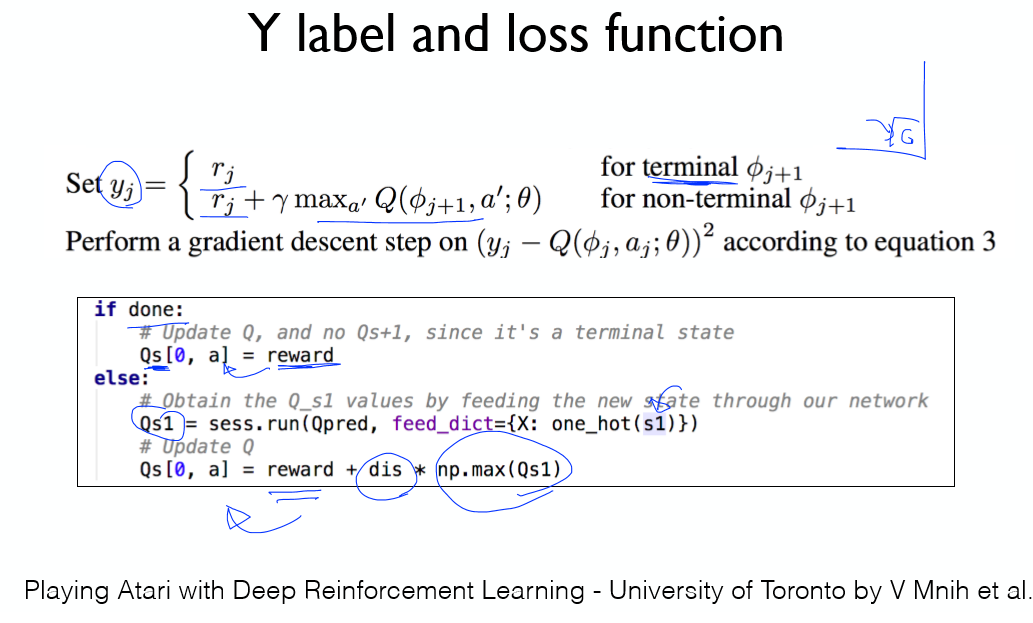
y값을 선택하는 알고리즘이다.

네트워크의 구성과 파라미터 설정
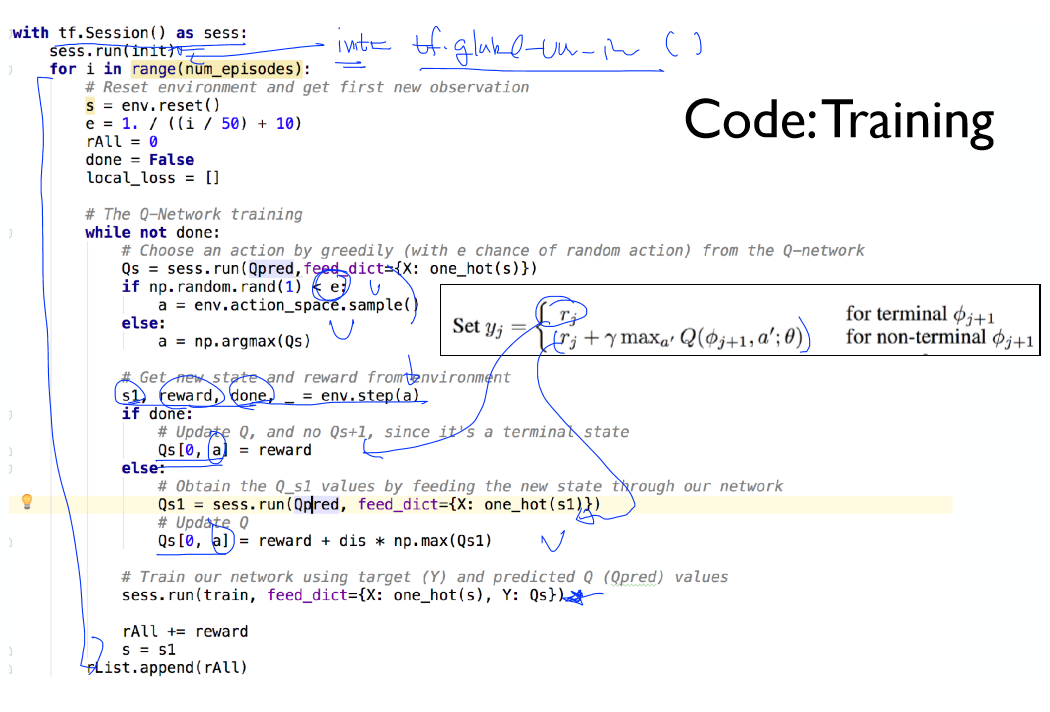
학습을 위한 코드.
현재 취한 Action에 대한 값만 수정하는 것을 볼 수 있다ㅑ.

Table을 이용한 결과보다 더 떨어지는 결과를 보인다.

* Array 추가 설명

입력의 크기는 1x16
가중치 배열의 크기는 16x4
출력값의 크기는 1x4 임을 확인!

Qs[a]라고 쓰는게 아닌 Qs[0, a]라고 써야한다!
구현 코드 (환경: ubuntu:16.04 python 3.6)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
import gym
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
env = gym.make('FrozenLake-v0')
# Input and output size based on the Env
input_size = env.observation_space.n
output_size = env.action_space.n
learning_rate = 0.1
# These lines establish the feed-forward part of the network used to
# choose actions
X = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, input_size], dtype=tf.float32) # state input
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform(
[input_size, output_size], 0, 0.01)) # weight
Qpred = tf.matmul(X, W) # Out Q prediction
Y = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, output_size], dtype=tf.float32) # Y label
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(Y - Qpred))
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(
learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(loss)
# Set Q-learning related parameters
dis = .99
num_episodes = 2000
# Create lists to contain total rewards and steps per episode
rList = []
def one_hot(x):
return np.identity(16)[x:x + 1]
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for i in range(num_episodes):
# Reset environment and get first new observation
s = env.reset()
e = 1. / ((i / 50) + 10)
rAll = 0
done = False
local_loss = []
# The Q-Network training
while not done:
# Choose an action by greedily (with e chance of random action)
# from the Q-network
Qs = sess.run(Qpred, feed_dict={X: one_hot(s)})
if np.random.rand(1) < e:
a = env.action_space.sample()
else:
a = np.argmax(Qs)
# Get new state and reward from environment
s1, reward, done, _ = env.step(a)
if done:
# Update Q, and no Qs+1, since it's a terminal state
Qs[0, a] = reward
else:
# Obtain the Q_s1 values by feeding the new state through our
# network
Qs1 = sess.run(Qpred, feed_dict={X: one_hot(s1)})
# Update Q
Qs[0, a] = reward + dis * np.max(Qs1)
# Train our network using target (Y) and predicted Q (Qpred) values
sess.run(train, feed_dict={X: one_hot(s), Y: Qs})
rAll += reward
s = s1
rList.append(rAll)
print("Percent of successful episodes: " +
str(sum(rList) / num_episodes) + "%")
plt.bar(range(len(rList)), rList, color="blue")
plt.show()
|
cs |
'공부 기록 > 모두를 위한 딥러닝 (RL)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7-1. DQN (0) | 2019.11.22 |
|---|---|
| 6-3. Q-Network 구현 (Cart Pole) (0) | 2019.11.21 |
| 6-1. Q-Network (0) | 2019.11.19 |
| 5-2. Windy Frozen Lake 구현 (0) | 2019.11.19 |
| 5-1. Windy Frozen Lake (Non-deterministic world) (0) | 2019.11.19 |
Comments




