| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 스위치
- Interrupt
- 디바이스 드라이버
- LED 제어
- 리눅스
- 신경망 첫걸음
- Switch
- GPIO
- 신경망
- 모두를 위한 딥러닝
- TensorFlow
- Linux
- Router
- 3분 딥러닝
- Network layer
- Generalized forward
- 모두를 위한 딥러닝]
- 운영체제
- demultiplexing
- LED
- Class Activation Map
- 밑바닥부터 시작하는 딥러닝
- RDT
- Transport layer
- 딥러닝
- 인터럽트
- 텐서플로우
- 펌웨어
- file descriptors
- function call
Archives
- Today
- Total
건조젤리의 저장소
12-4. Tensorflow를 이용한 RNN + Softmax layer 구현 본문
김성훈 교수님의 강의내용을 정리한 내용입니다.
출처 : http://hunkim.github.io/ml/
모두를 위한 머신러닝/딥러닝 강의
hunkim.github.io
앞의 내용에서는 길이가 매우 긴 문장의 경우 결과값이 제대로 나오지 않는다고 하였다.
이를 해결하기 위해서는 어떻게 해야할까?

RNN구조를 더 쌓아 깊은 구조로 만들게 된다면 성능이 더 좋아질 것이다.
MultiRNNCell 명령어를 이용하면 여러개의 층을 쌓을 수 있다.
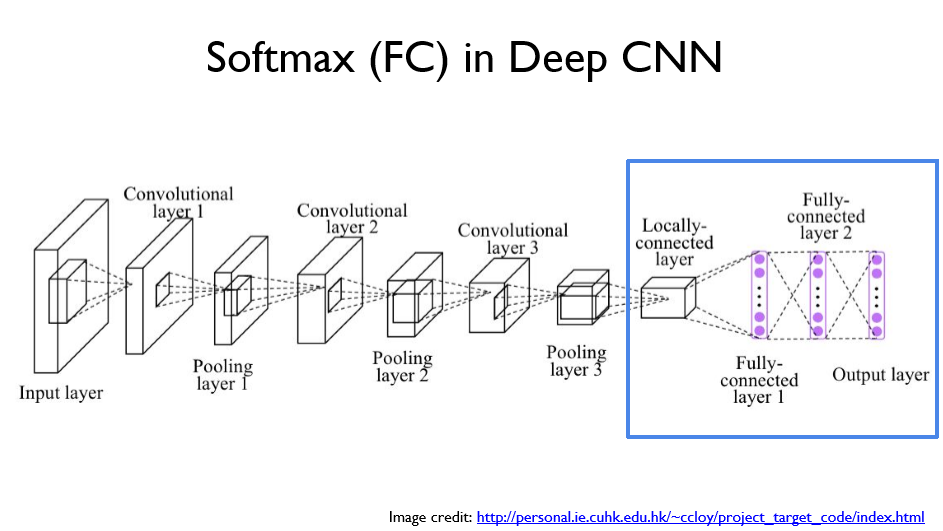
CNN구조의 끝 부분에는 FC 레이어가 존재한다. 이를 RNN에도 적용시켜보자.
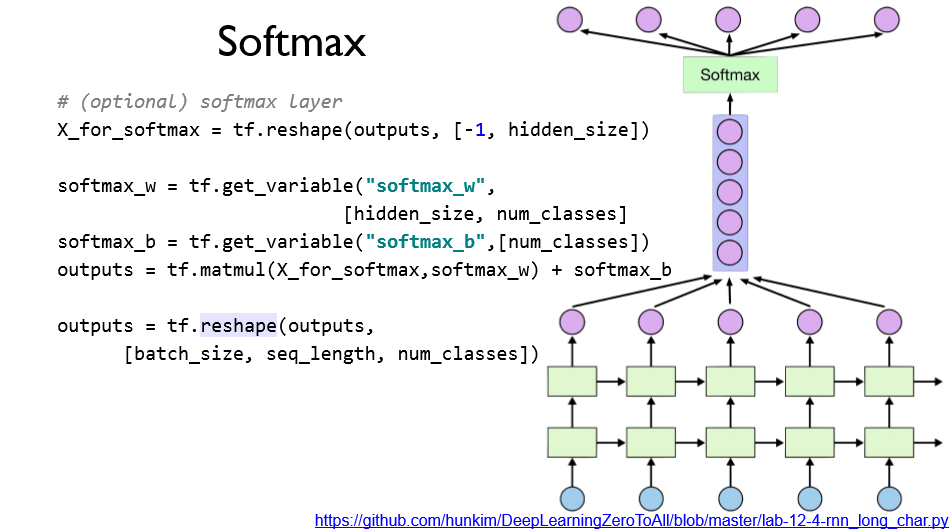
softmax를 RNN에 붙여 결과를 출력하는 형태이다.
이를 위해서 RNN의 출력 결과를 reshape를 통해 나열한 뒤 FC 구조를 통과시킨다,
이후 다시 원래의 모양으로 되돌려준다.
아직 Softmax함수를 적용하지 않음을 알 수 있는데,
이는 Cost Fucntion인 sequence_loss 함수 안에 구현이 되어 있기 때문이라고 한다.


이제 outputs을 출력하면 Cost가 낮아지며 결과도 좋아지는 것을 확인할 수 있다.

최종 결과, 출력 결과는 매우 유사하게 나타난다.
코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
|
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
tf.set_random_seed(777) # reproducibility
sentence = ("if you want to build a ship, don't drum up people together to "
"collect wood and don't assign them tasks and work, but rather "
"teach them to long for the endless immensity of the sea.")
char_set = list(set(sentence))
char_dic = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(char_set)}
data_dim = len(char_set)
hidden_size = len(char_set)
num_classes = len(char_set)
sequence_length = 10 # Any arbitrary number
learning_rate = 0.1
dataX = []
dataY = []
for i in range(0, len(sentence) - sequence_length):
x_str = sentence[i:i + sequence_length]
y_str = sentence[i + 1: i + sequence_length + 1]
print(i, x_str, '->', y_str)
x = [char_dic[c] for c in x_str] # x str to index
y = [char_dic[c] for c in y_str] # y str to index
dataX.append(x)
dataY.append(y)
batch_size = len(dataX)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, sequence_length])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, sequence_length])
# One-hot encoding
X_one_hot = tf.one_hot(X, num_classes)
print(X_one_hot) # check out the shape
# Make a lstm cell with hidden_size (each unit output vector size)
def lstm_cell():
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(name='basic_lstm_cell', num_units=hidden_size, state_is_tuple=True)
return cell
multi_cells = rnn.MultiRNNCell([lstm_cell() for _ in range(2)], state_is_tuple=True)
# outputs: unfolding size x hidden size, state = hidden size
outputs, _states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(multi_cells, X_one_hot, dtype=tf.float32)
# FC layer
X_for_fc = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, hidden_size])
outputs = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(X_for_fc, num_classes, activation_fn=None)
# reshape out for sequence_loss
outputs = tf.reshape(outputs, [batch_size, sequence_length, num_classes])
# All weights are 1 (equal weights)
weights = tf.ones([batch_size, sequence_length])
sequence_loss = tf.contrib.seq2seq.sequence_loss(
logits=outputs, targets=Y, weights=weights)
mean_loss = tf.reduce_mean(sequence_loss)
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(mean_loss)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(500):
_, l, results = sess.run(
[train_op, mean_loss, outputs], feed_dict={X: dataX, Y: dataY})
for j, result in enumerate(results):
index = np.argmax(result, axis=1)
print(i, j, ''.join([char_set[t] for t in index]), l)
# Let's print the last char of each result to check it works
results = sess.run(outputs, feed_dict={X: dataX})
for j, result in enumerate(results):
index = np.argmax(result, axis=1)
if j is 0: # print all for the first result to make a sentence
print(''.join([char_set[t] for t in index]), end='')
else:
print(char_set[index[-1]], end='')
|
cs |
'공부 기록 > 모두를 위한 딥러닝 (Basic)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 12-6. RNN with time series data (stock) (0) | 2019.11.14 |
|---|---|
| 12-5. Dynamic RNN (0) | 2019.11.14 |
| 12-3. Tensorflow를 이용한 RNN 예제 실습 (0) | 2019.11.13 |
| 12-2. Tensorflow를 이용한 RNN 기초 실습 (0) | 2019.11.13 |
| 12-1. RNN (0) | 2019.11.13 |
Comments




